Animal models are often used when trying to study the possible effects of a medication or treatment and subsequently extrapolated to humans. Which species is selected depends on what is being studied. 🕖 Reading Time, 4 minutes Guinea Pigs Nerve …
🕖 Reading Time, 3 minutes In 2017, the CDC issued an emergency use authorization for a new atropine auto-injector manufacturing company because there was a sense there were not enough atropine auto-injectors in the national stockpile. Atropine is the standard …
If you are going to carry a tourniquet, we feel two is the minimum load-out carried on the body. 🕖 Reading Time, 3 minutes The best data available indicates a 70% occlusion rate of a single tourniquet on a volunteer …
CAT Environmental Breakage 🕖 Reading Time, 3 minutes We receive frequent questions about shelf-life and environmental degradation of tourniquets. There has been some discussion in the US Department of Defense about declaring a five-year self-life for new, unused commercial tourniquets …
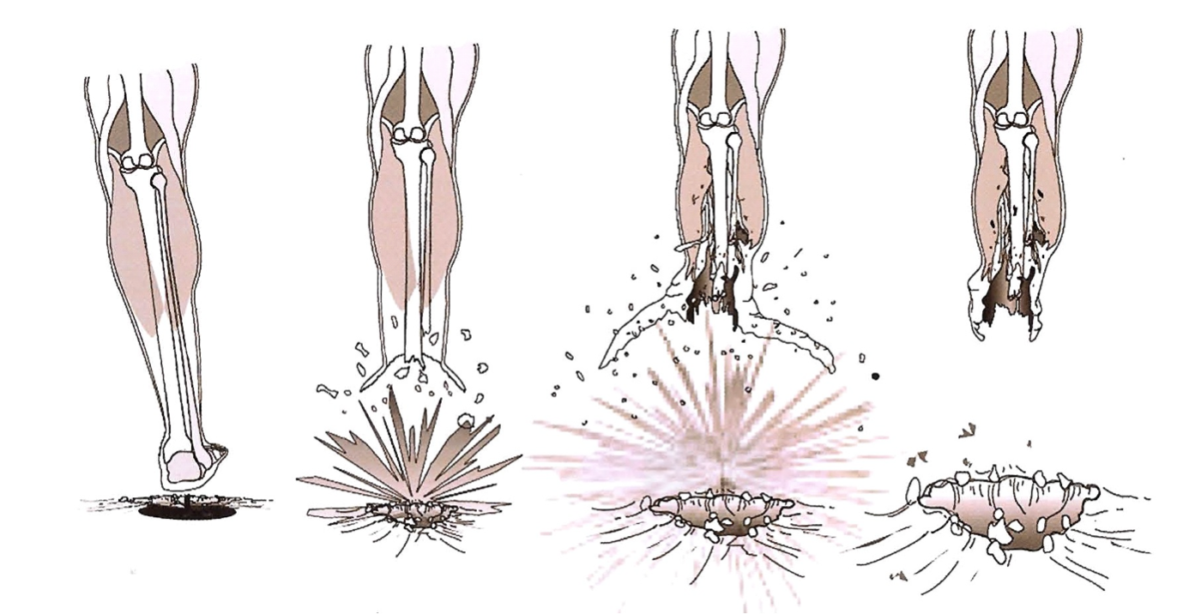
🕖 Reading Time, 9 minutes When a casualty steps on a blast mine or is very close to an explosive charge, the explosive force travels up the leg/limb of the casualty stripping skin, fascia, and muscle off the bone. This …
BLUF*: Hypotensive trauma patients need the cause of their hypotension fixed: whether that is aggressive hemorrhage control, administration of blood products, or needle decompression for tension pneumothorax. IVF is a very temporary fix; blood products would be better. Push dose …