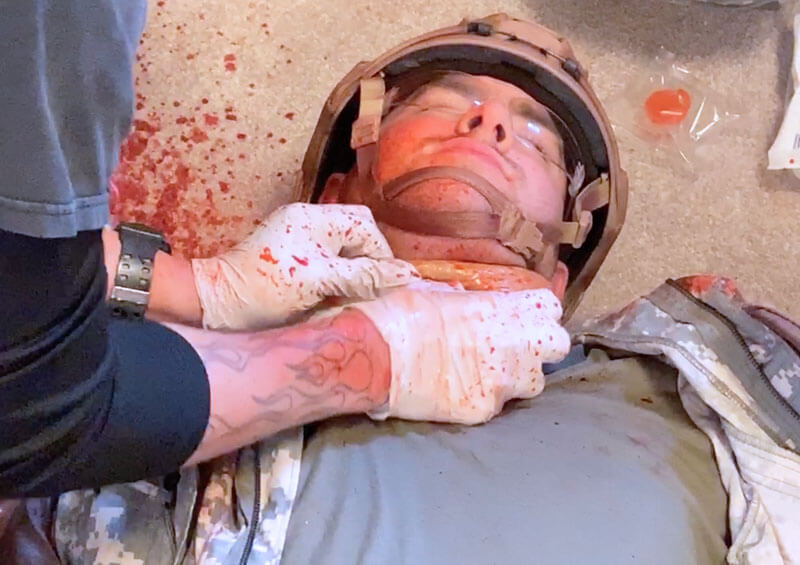
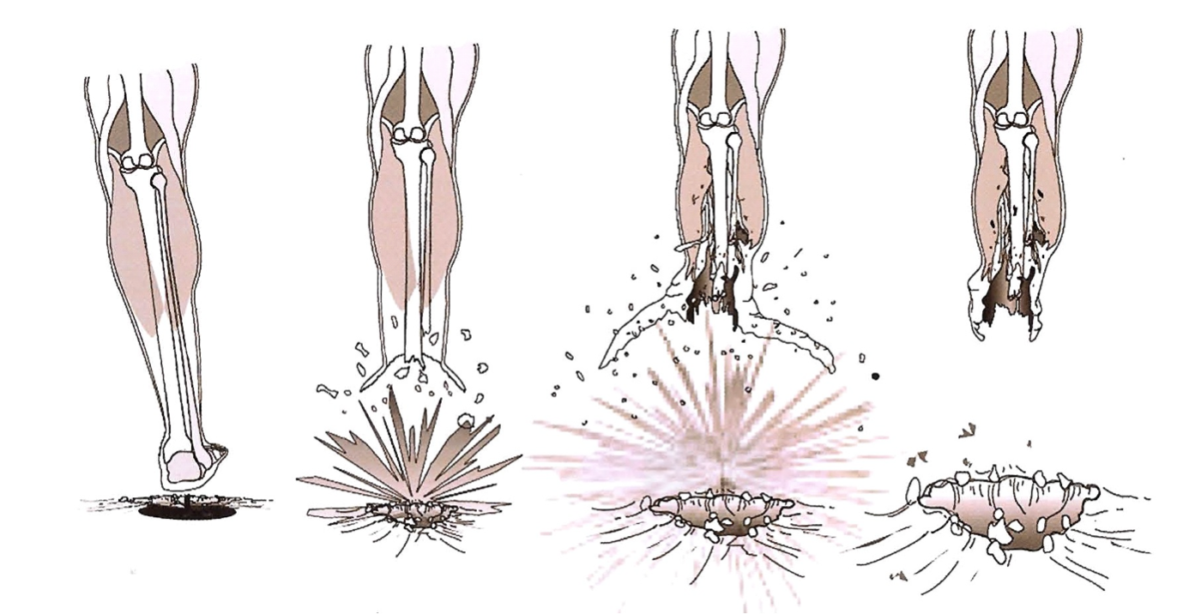
🕖 Reading Time, 9 minutes When a casualty steps on a blast mine or is very close to an explosive charge, the explosive force travels up the leg/limb of the casualty stripping skin, fascia, and muscle off the bone. This …
MARCH: Massive Hemorrhage, Airway, Respiration, Circulation, Hypothermia Prevention
The easy to remember mnemonic MARCH reminds us of the priorities in treating casualties during TECC and TCCC situations. MARCH provides a framework to address immediate life threats and gives an organized approach to begin a casualty evaluation. The MARCH mnemonic is preferable to the ABCDE model because it takes into consideration the reason you need an airway and to be breathing is to circulate blood to the casualty’s brain. Recognizing that, the first step in our casualty evaluation should be to look for massive hemorrhage.
Once past massive hemorrhage, A-R-C is loosely approximated by A-B-C. H- is a reminder that a large number of traumatic casualties arrive at the emergency department or medical treatment facility hypothermic which dramatically increases their death rate.
The MARCH mnemonic can be applied to any patient, as the initial casualty evaluation usually rules out massive hemorrhage.
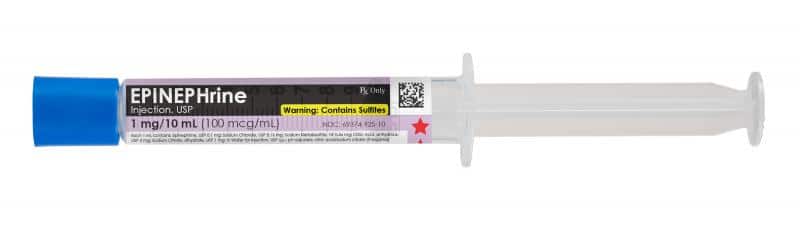
BLUF*: Hypotensive trauma patients need the cause of their hypotension fixed: whether that is aggressive hemorrhage control, administration of blood products, or needle decompression for tension pneumothorax. IVF is a very temporary fix; blood products would be better. Push dose …
🕖 Reading Time, 3 minutes While helping teach a class with InSights Training Center at West Coast Armory Indoor Range, I was really impressed to see they posted emergency instructions in the event of a training accident if 911 must …
The term “junctional hemorrhage” refers to injuries and bleeding occurring at the transition zones between the extremities and the torso. 🕖 Reading Time, 4 minutes The term first appeared in the medical literature in December 2009. Although not an extremity, …
🕖 Reading Time, 5 minutes There is nothing like a brief stay in recently war-torn Portland, Oregon, to force you to rethink your security and tactical medical support plan in a high-risk environment. If you consider yourself a competent tactical …
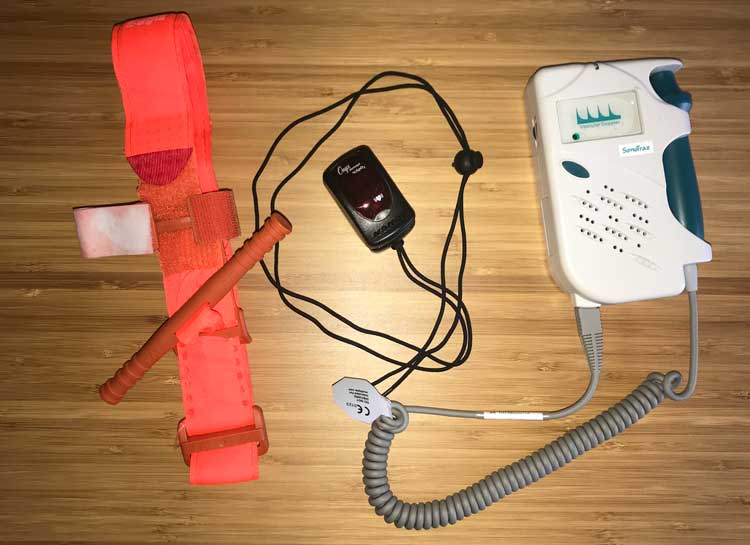
🕖 Reading Time, 5 minutes BLUF:* Is there a role for using a fingertip pulse oximeter as a training tool for tourniquet placement? We believe the answer is no. Considering the relative expense of a quality, FDA approved model pulse ox, a …